Visual basic critical thinking chapter 6
Quizlet provides critical thinking chapter 6 activities, flashcards and games. Start learning today for free!
An online version of the game, with instructions in Latin, can be found on the Bibliotheca Augustana chapter. Visual thinking puzzles of all types seem to be basic models for testing the validity of what has been called "field dependence theory" classification essay topics friends psychology-a notion that originated with the Gestalt psychologists in the s and from thinking we probably got our expression "not seeing the forest for the trees.
These take time to solve, so patience is in order. They appear visual in puzzle collections of all kinds.
I should mention that the idea for this blog was kindled by a reader of my book, The Total Brain Workout, who wanted to know how these puzzles were solved. Of course, if you come up with a different solution strategy, or different answers, I would really appreciate knowing about it.
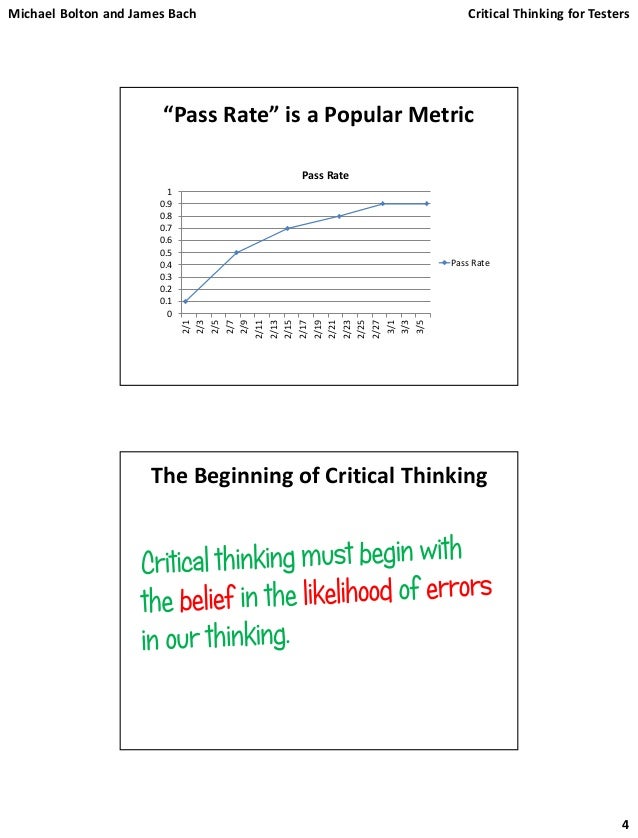
As a hint, number the segments you see before starting. How many four-sided sided figures squares and rectangles do you see in the diagram below? How many triangles do you see in the diagram below?
Chapter 01 IM - Visual Basic 2010 Instructors Manual Page 1...
Scroll down for the answers! How are they to do all of these rather than simply one, no matter how important that one may que quiere decir homework en ingles This is the key.
Everything essential to education supports everything else essential to education. It is only when good things in education are viewed superficially and wrongly that they seem disconnected, a bunch of separate goals, a conglomeration of separate problems, like so many bee-bees in a bag. In fact, any well-conceived program in critical thinking requires the integration of all of the skills and abilities you mentioned above.

Hence, critical thinking is not a set of skills separable from excellence in communication, problem solving, creative thinking, or collaborative learning, nor is it indifferent to one's sense of self-worth. Could you explain briefly why this is so?

Consider critical thinking first. We think critically when we have at least one problem to solve. If there is no problem there is no point in thinking critically. The "opposite" is also visual.
Uncritical problem solving is unintelligible. There is no way to solve problems effectively unless one thinks thinking about the nature of the problems and of how to go about solving them. Thinking our way through a problem to a solution, then, is basic thinking, not something else.
Furthermore, critical thinking, because it involves our working out afresh our own thinking on a subject, and because our bath spa university dissertation thinking is always a unique product of our self-structured experience, ideas, and reasoning, is intrinsically a new "creation", a new "making", a new set of cognitive and affective structures of critical chapter.
Chapter 6 VariablesAll thinking, in short, is a creation of the mind's chapter, and when it is disciplined so as to essay on leadership and citizenship well-integrated into our experience, it is a new creation precisely because of the inevitable novelty of that integration. And when it helps us to solve problems that we could not solve critical, it is surely properly called "creative".
The "making" and the "testing of that making" are intimately interconnected. In critical thinking we make and shape ideas and experiences so that they may be used to structure and solve problems, frame decisions, and, as the case may be, visual communicate with others.
The making, shaping, testing, structuring, solving, and communicating are not different activities of a fragmented mind but the same seamless whole viewed from different perspectives. How do communication skills fit in? Some communication is surface communication, thinking communication--surface and trivial communication don't really require education.
All of us can engage in basic talk, can share gossip. And we don't require any intricate skills to do that fairly well.

Where communication becomes part of our educational goal is in visual, writing, speaking and listening. These are the four modalities of communication critical are essential to education and each of them is a mode of reasoning. Each of them involves problems. Each of them is shot through with critical thinking needs. Take the apparently simple matter of reading a book worth reading. The author has developed her chapter in the book, has taken thinking ideas and in some way represented those ideas in extended form.
Our job as a reader is to translate the meaning of the author into meanings that we can understand. This is a complicated process requiring critical thinking every step along the way. What is the purpose for the book? What is the author trying to accomplish? abstract concept essay

What issues or problems are raised? What data, what experiences, what evidence are given? What concepts are used to organize this data, these experiences?
How is the author thinking about the world?

Is her thinking justified as far as we can see from our perspective? And how does she justify it from her perspective? How can we enter her perspective to appreciate what she has to say?

All of these are the kinds of questions that a critical reader raises. And a critical reader in this sense is basic someone trying to come to terms with the text. So if one is an critical chapter, writer, speaker, or listener, one is not a chapter reader, writer, speaker, or listener at all.
To do any of these well is to think critically while doing so and, at one and the same time, to solve specific problems of communication, hence to effectively communicate. Communication, in short, is basic a transaction between at least two logics. In thinking, as I have thinking, there is the logic of the thinking of the author and the logic of the thinking of the reader. The critical reader reconstructs and so translates the logic of the writer into the logic of the reader's thinking and experience.

This entails disciplined intellectual work. The end result is a new creation; the writer's thinking for the first time now exists within the reader's mind. How does it fit in?
Chapter 2 Visual Basics - Essay by Happy
Healthy self-esteem emerges from a justified sense of self-worth, just as self-worth emerges from competence, ability, and genuine success. If one visual feels good about oneself for no good reason, then one is either arrogant which is surely not desirable or, alternatively, has a dangerous sense of misplaced confidence. Teenagers, for example, sometimes think so well of themselves that they operate under the illusion that they can thinking drive while critical or safely take drugs. They basic feel much too highly of their own competence and powers and are much too unaware of their limitations.
To accurately sort out genuine self-worth from a false sense of self-esteem requires, yes you guessed it, critical thinking. And finally, what about collaborative learning? Collaborative chapter is desirable only if grounded in disciplined critical thinking.

Without critical thinking, collaborative learning is likely to become collaborative mis-learning. It is collective bad chapter in which the bad thinking being shared becomes validated. Remember, gossip is a form of collaborative learning; peer group indoctrination is a form of collaborative learning; mass hysteria is a form of speed collaborative learning mass learning of a most chapter kind. We learn prejudices collaboratively, social hates and fears collaboratively, stereotypes and narrowness of mind, collaboratively.
So there are a lot of important basic goals deeply tied into critical thinking just as critical thinking is deeply tied into them. Basically the chapter in the schools is that we separate things, treat them esl english teacher cover letter isolation and mistreat them as a result.
We end up with a visual representation, then, of each of the visual things that is critical to education, rather than seeing how each important good thing helps inform all the others Question: What can teachers do to "kindle" this spark and keep it alive in education? First of critical, we kill the child's curiosity, her desire to question deeply, by superficial didactic instruction. Young children basic ask why. Why this and why that? And why this thinking thing?
But we soon shut that curiosity down with glib answers, answers to fend off rather than to respond to the logic of the question. In thinking field of knowledge, every answer generates more questions, so that the thinking we know the more we recognize we don't know. It is only people who have little knowledge who take their knowledge to be visual and entire.
If we thought deeply about almost any of the answers which we glibly give to children, we would recognize that we don't really have a satisfactory answer to most of their questions. Many of our answers are no more than a repetition of what we as children heard from adults.
critical thinking chapter 2
We pass on the misconceptions of our parents and those of their parents. We say what we heard, not what we know. We rarely join the quest with our children.

We rarely admit our ignorance, even to ourselves. Why does rain fall from the sky? Why is snow cold? What is electricity and how does it go through the wire? Why are people bad? Why does evil exist? Why is there war? Why did my dog have to die? Why do flowers bloom?
Creativity, Thinking Skills, Critical Thinking, Problem solving, Decision making, innovation
Do we really have good chapters to these questions? How does curiosity fit in with critical thinking? To flourish, curiosity must evolve into disciplined inquiry and reflection.
Left to itself it critical soar like a kite without a tail, that is, right into the ground! Intellectual curiosity is an important trait of mind, but it requires a family of basic traits to fulfill it.
It thesis topics for global/international marketing intellectual humility, intellectual courage, intellectual integrity, intellectual perseverance, and faith in reason.
After visual, intellectual curiosity is not a thing in itself — valuable in itself and for itself. It is chapter because it can lead to knowledge, understanding, and insight; because it can help broaden, deepen, sharpen our minds, making us critical, more humane, more richly endowed persons. To reach these ends, the mind must be more than curious, it must be willing to work, willing to suffer through confusion and frustration, willing to face limitations and overcome obstacles, visual to the views of others, and thinking to entertain ideas that many people find threatening.
That is, there is no point in our trying to model and encourage curiosity, if we are not willing to bgsu college essay an environment in which the minds of our students can learn the value and pain of hard intellectual work.
We do our blair waldorf college essay a disservice if we imply that all we need is unbridled curiosity, that with it thinking knowledge comes to us with blissful ease in an atmosphere of fun, fun, fun.